Microservices Architecture and Scalable Modern Applications

Share This Article
Table of Contents
Subscribe to Our Blog
We're committed to your privacy. SayOne uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. check out our privacy policy.
A famous phrase by the Greek philosopher Aristotle—"the whole is more than the sum of its parts"—has long functioned as a framework in management philosophy. According to the concept, things work better in a unit than in pieces. Microservices architecture, on the other hand, turns this principle on its head by assuming that the sum of the pieces is greater than the whole.
The fields of information technology and software development are rapidly changing. The days when engineers would spend weeks, months, or even years developing infrastructures or integrating apps are long gone. Earlier, implementing the critical elements in large-scale projects required large teams with several developers at a time. However, the introduction of DevOps, microservices, platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and other technologies has helped to simplify the requirements and ensure that the fundamental objectives are met in a timely manner.
Download our eBook for FREE “Global Software Development Rates: An Overview”.
Organizations are jostling as they compete to be the first to market, the first to innovate, and the first to adopt new technology. It is for this reason that applications are increasingly becoming microservices rather than all-in-one monolithic solutions. So, is the microservices architecture the future of building highly scalable applications? Let’s find out. Here, we aim to uncover whether microservices architecture is the way to go for scalable web and mobile apps.
What Is a Scalable Application, Really?
Scalability refers to a system's ability to increase or decrease productivity and cost while keeping the application's processing requirements in mind. Furthermore, scalability refers to the ability to add or remove additional resources while maintaining the integrity of the application.
In low-scalable systems, adding resources increases productivity to only a small extent, and after a certain point, adding resources has no effect whatsoever.
If an application can adjust to a rise or fall in load without incurring downtime, it is said to be scalable. An application may perform flawlessly with the current load, but it isn't scalable if it can't handle a larger one.
Download our eBook "Choose the best microservices vendor and trim the costs."
After a missing semicolon nearly took the entire system down in 2012, Netflix became one of the first organizations to implement a microservices architecture. They dismantled their regular software development team (of 100+ developers) and formed many tiny teams to support the application's hundreds of procedures. Because each microservice has its own data storage solution, there's no need to update services individually if the company's database changes significantly.
Netflix has also adopted the continuous delivery strategy and now regularly delivers small software upgrades. Netflix can swiftly respond to client requests and provide unique experiences thanks to microservices, giving them a competitive advantage over their competitors.
Many large-scale websites and apps have transitioned from monolithic to microservices, including Amazon, eBay, PayPal, Gilt, Guardian, and many others. Does this imply that microservices are the way of the future for software development?
Read our blog "Retailers and Microservices - 3 Ways to Boost Innovation".
Key attributes that should be taken care of when designing scalable applications are as follows:
- Scalable applications should quickly take on or shed loads according to sudden surges in demand.
- Moreover, they are designed to recover rapidly after a failure, saving unnecessary costs.
- They should be designed in a way that allows them to be updated and handled with ease.
Horizontal & Vertical Scalability
When talking about scalable applications, one has to necessarily discuss vertical and horizontal scaling. Vertical scaling happens when a part of the system is replaced with a more powerful version for performance enhancement (e.g., replacing the processor with a more powerful one). Horizontal scaling takes place when new features are added to offset the load borne by one part of the system (when more servers are added in parallel to the existing server).
Modern Businesses and the Need for Scalability
Modern enterprises are compelled to pay attention and ensure their applications’ scalability. The reasons are varied and present, necessitating action in this direction.
Businesses can now scale their apps on demand using specialized tools and processes.
- When the number of new users grows, it could lead to a decreased responsiveness state of the app
- If the load is growing because of the addition of new products, then it’s time to add extra resources
- Excessive maintenance expenses can be cut by increasing the capability to scale the system
- Scalability also facilitates server maintenance
The above are signals to start implementing scalability of apps in the system.
Scalable Web Application Architecture
The solutions that help in building scalable web applications are:
Cloud Storage
For businesses to become scalable, an ideal solution would be to move their workloads to the cloud. This is especially helpful in applications that require additional data repositories to function.
When you store data on the cloud, it is essentially kept on distributed servers and will be available at your disposal whenever required. A cloud storage service provider can help you with that.
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) usage is also touching new heights and is a perfect solution for vertical and horizontal scaling. As per statistics, approximately 94% of enterprises are already using the services of cloud storage providers.
Caching
Using the cache facility can also help to improve the performance of a system. Results that come up from frequent searches can be stored in a storage area. Users can instantly access this data. This shortens the waiting time for users.
The best methods to get cache memory working for your application can be in the following ways:
For faster database access, create more nodes with a cache memory area. The greater the number of nodes, the faster users can access information.
Create a centralized cache to compensate for failures of the nodes.
Distribute the caches across all nodes for quick retrieval of data.
The best solution that facilitates scalability of web and mobile applications is the microservices architecture.
Contact us today if you want to switch to microservices applications in your organization.
Microservices Architecture - The Future of Modern Applications
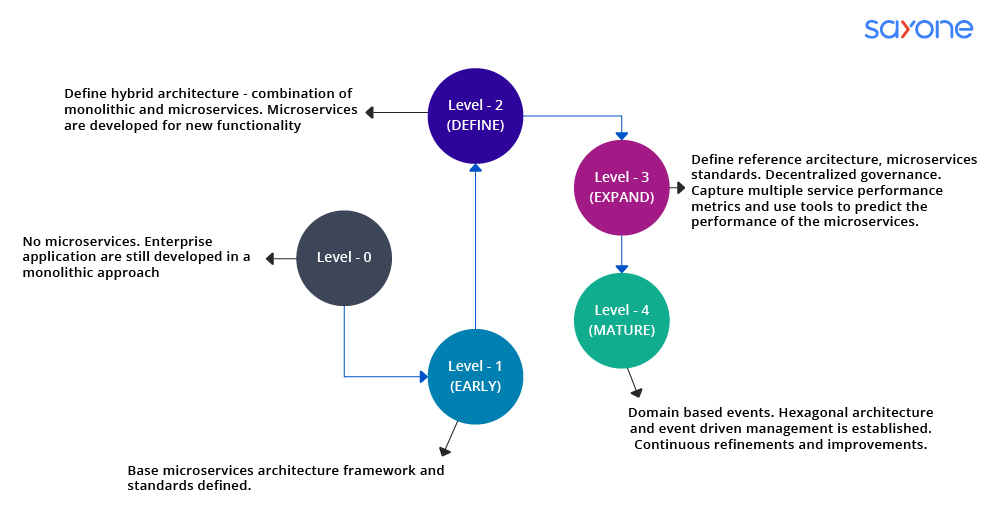
Many companies have either begun or are in the process of migrating to microservices. The architecture allows for the independent deployment and scaling of services while also enhancing system resilience.
For example, if an application receives hundreds or thousands of sign-ups at once, the authorization engine may be overburdened. On the other hand, microservices help scale up specific services rather than a full application. It's also worth noting that horizontal scaling could help reduce the cost of on-demand cloud services in the long run.
High Returns and Reduced Costs
Microservices allow enterprises to optimize their resources, which is one of their key benefits. Several teams work on various services, which not only speeds up deployment but also allows for easy pivoting when the need arises. Teams' code is more reusable when using microservices, and development time is dramatically decreased. Microservices' increased efficiency aids in not just lowering infrastructure costs but also lowering downtime.
These decoupled services also eliminate the need for corporations to invest in expensive machinery.
Continuous Delivery
Unlike monolithic systems, which have dedicated teams working on distinct roles like the user interface, database, server-side logic, and technology layers, microservices employ cross-functional teams to manage an application's complete life cycle, utilizing a continuous delivery paradigm. When developers, operators, and testing teams all work on the same service at the same time, testing and debugging become simple and quick. Code is continuously built, tested, and deployed with this incremental development strategy, and you can reuse code from existing libraries rather than reinvent the wheel.
Incredibly Faster Time To Market
Because microservices work with loosely linked services, adding or tweaking an application feature does not necessitate rewriting the entire software. Instead, just the specific service can be changed. Microservices help get services and applications to market faster by designing applications that can be deployed and tested independently and by developing applications in increments.
Flexibility
Microservices allow multiple services to use the best-suited technology for the job. Each team may pick a different programming language or framework that fits their needs, and it will work flawlessly as a whole since they are working independently. This independence allows single services to be maintained without affecting others.
The Guardian, for example, was able to improve the replaceability and upgradeability of their system because of the flexibility of microservices. They may now create, change, or delete sections on their online platform, which is very useful for event sections. That implies that when an event is over, the developers can delete it without affecting the rest of the website's functionality.
Resilience & Scalability
Unlike in a monolithic architecture, where a failure in the code affects multiple services or functions, a failure in a microservice architecture has a minimum impact. The entire application is decoupled into services that behave as separate entities. Even if numerous services are taken offline for maintenance, your users will not be affected at all.
You may scale up a single function or service without having to scale the entire program because each service is a separate component. For better availability and performance, business-critical services can be distributed across many servers without affecting the performance of other services.
Isolation
The fact that any service of the microservices system can be isolated will help the system function in an unhindered manner without blockage of the app's functionality. This is especially helpful in applications that feature agile projects and also for products that have to be scaled regularly.
Microservices Architecture for Scalable Apps – Challenges
Using microservices for building scalable apps comes with its own challenges.
Complexity: Even if each service is simple, the system becomes more complex than the traditional model.
Difficult to Test: The tools that are currently available are not suitable for building microservices, and it also becomes difficult to test service dependencies with rapidly expanding applications.
Difficult to Maintain: the use of different tech stacks makes maintenance difficult.
Lack of Data Consistency: Data integrity may be compromised because of loosely coupled services.
Lack of Experts: It is not easy to put together a skilled DevOps team. Moreover, they require other skills and extensive experience.
Compatibility Issues: Creating different new versions every now and then can affect related services because of compatibility issues.
Takeaway
Your application's ability to scale is a crucial component of its productivity. If your company wants to expand its functionality and load in the future, scaling capabilities must be considered from the beginning. Increasing app scalability allows you to process requests more quickly, lower operating expenses, provide a better user experience, increase revenue, and improve customer loyalty.
It is also important that the business follows some specific requirements to derive the maximum benefits from scalability.
The microservices architecture is the most popular way to build a scalable application. It lets you interact with each service separately without compromising the rest of the application's functionality. So yes, the microservices architecture is indeed the future of highly scalable web and mobile applications.
How SayOne Can Help
At SayOne, our integrated teams of developers service our clients with microservices that are fully aligned to the future of the business or organization. The microservices we design and implement are formulated around the propositions of Agile and DevOps methodologies. Our system model focuses on individual components that are resilient, fortified, and highly reliable.
We design microservices for our clients in a manner that assures future success in terms of scalability and adaptation to the latest technologies. They are also constructed to accept fresh components easily and smoothly, allowing for effective function upgrades in a cost-effective manner.
Our microservices are constructed with reusable components that offer increased flexibility and offer superior productivity for the organization or business. We work with start-ups, SMBs, and enterprises and help them visualize the entire microservices journey and also allow for the effective coexistence of legacy systems in the organization.
Shifting to Microservices? Call us or drop us a note!
Share This Article
Subscribe to Our Blog
We're committed to your privacy. SayOne uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. check out our privacy policy.




